What Are Wildfire Events?
Definition of Wildfire Events
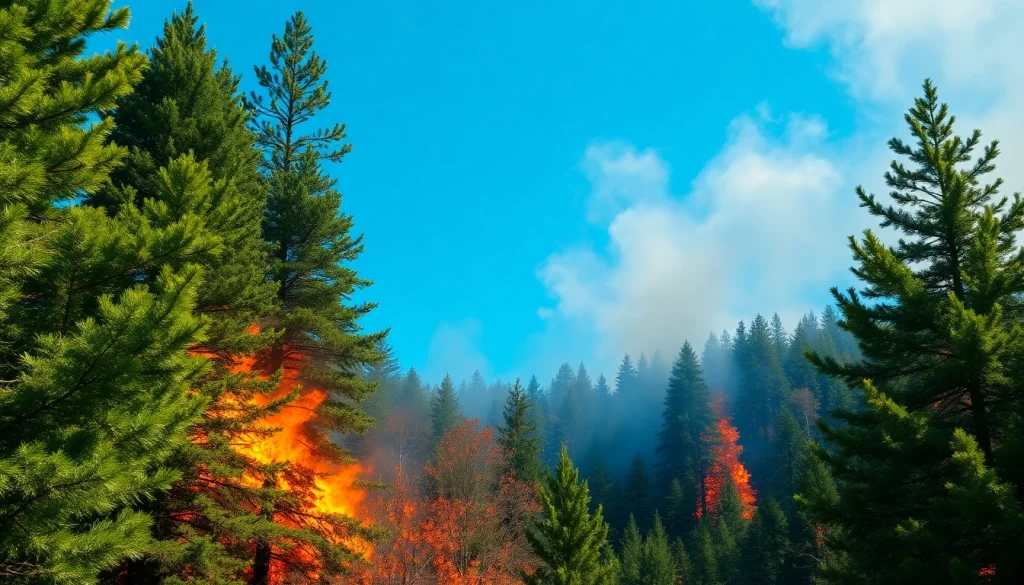
Wildfire events refer to uncontrolled fires that primarily occur in wildland areas, encompassing forests, grasslands, and shrublands. These events can spread quickly, fueled by dry conditions, wind, and available vegetation. Wildfires can be ignited by natural causes such as lightning or human activities, including campfires, discarded cigarettes, or intentionally set fires. Understanding Wildfire events is crucial for developing effective prevention and response strategies.
Causes of Wildfire Events
The causes of wildfire events can essentially be categorized into two primary sources: natural and human-induced.
- Natural Causes: Lightning strikes are often the leading cause of natural wildfire events. Drought conditions, high temperatures, and winds can exacerbate these incidents, facilitating the spread of fire.
- Human Factors: About 85% of wildfires are initiated by human activity. Common causes include campfires left unattended, discarded cigarettes, sparks from machinery, and intentional arson.
Types of Wildfire Events
Wildfires can be classified into various types based on their behavior and effects:
- Surface Fires: These are the most common types, burning through litter, small plants, and shrubs while allowing larger trees to often survive.
- Crown Fires: These fires leap from treetop to treetop and consume the entire forest canopy, often resulting in extensive damage.
- Ground Fires: These occur underground, burning organic material in the soil and can smolder for long periods before emerging as surface fires.
- Wildland Fires: This term encompasses all fires occurring in wildland areas regardless of cause, character, or intensity.
The Ecology of Wildfire Events
Natural Role of Wildfire Events in Ecosystems
Wildfire events play a complex role in the ecology of various ecosystems. While often perceived as destructive, fires are essential for maintaining healthy forests and habitats. They help in:
- Regeneration: Many species, including certain pine trees, depend on fire for seed germination.
- Restoration of Nutrients: Fires facilitate the breakdown of dead organic material, enriching the soil with nutrients.
- Promotion of Biodiversity: By creating a mosaic of different habitats, fires can enhance habitat diversity and support a range of flora and fauna.
Impact on Biodiversity during Wildfire Events
The aftermath of wildfire events can significantly affect biodiversity. While some species thrive post-fire, the immediate impacts can be devastating. Habitat loss can lead to reduced populations of species unable to adapt or relocate. However, many ecosystems have adapted to fire, relying on periodic burns to weed out non-native species and promote the growth of fire-resistant plants.
Recovery and Renewal after Wildfire Events
The recovery process following a wildfire can vary greatly depending on the severity of the fire and the resilience of the ecosystem. Typically, the stages include:
- Colonization: Soon after a fire, pioneer species such as grasses and wildflowers begin to cover the burnt areas.
- Intermediate Stage: As time progresses, shrubs and young trees will emerge, slowly re-establishing the habitat.
- Climax Stage: Ultimately, a mature ecosystem develops, which can take decades or even centuries, depending on the species involved.
Wildfire Events and Climate Change
Increasing Frequency of Wildfire Events
Climate change has dramatically influenced the frequency and intensity of wildfire events globally. Rising temperatures, extended droughts, and shifting precipitation patterns create ideal conditions for wildfires to ignite and spread. Regions previously less susceptible to wildfires are now facing increased risks, leading to a surge in incidents affecting both natural and urban areas.
Climate Factors Influencing Wildfire Events
Various climate factors contribute to the occurrence and severity of wildfire events:
- Temperature: Higher average temperatures can increase the likelihood of fires by drying out vegetation.
- Drought: Extended dry periods reduce moisture in vegetation, making it more flammable.
- Wind Patterns: Wind can carry embers over long distances, resulting in spot fires far from the original blaze.
Strategies to Mitigate Impact of Wildfire Events
Mitigation strategies are essential to minimize the impacts of wildfire events. These include:
- Fuel Management: Techniques such as controlled burns or mechanical removal of flammable vegetation can lessen fuel loads.
- Community Preparedness Programs: Educating and preparing communities can enhance resilience and reduce risks.
- Improved Building Codes: Implementing fire-resistant building materials and designs can protect structures in fire-prone areas.
Community Preparedness for Wildfire Events
Essential Steps for Wildfire Events Readiness
Community preparedness is critical for ensuring safety during wildfire events. Essential steps include:
- Creating Emergency Plans: Each household should have an actionable emergency plan detailing evacuation routes and communication methods.
- Establishing Defensible Space: Residents should create defensible zones by clearing vegetation and maintaining a safe distance from structures.
- Staying Informed: Communities should maintain awareness of a wildfire risk through local alerts and updates.
Role of Local Authorities in Managing Wildfire Events
Local authorities play a crucial role in wildfire risk management. Their responsibilities include:
- Monitoring and Reporting: Authorities must monitor weather conditions and report immediate risks to residents.
- Clear Communication: Open channels of communication help disseminate critical information during a wildfire.
- Training and Resources: Providing training to community members on fire safety and emergency response can enhance local resilience.
Community Initiatives for Wildfire Events Awareness
Awareness initiatives can greatly improve community readiness. Examples include:
- Public Education Workshops: Organizing workshops on fire risks and safety practices fosters community knowledge.
- Collaboration with Local Organizations: Partnering with non-profits and schools to promote wildfire education initiatives.
- Events for Volunteer Firefighters: Engaging community members in volunteer firefighting training can empower local response capabilities.
FAQs About Wildfire Events
What Is the Most Known Wildfire Event?
The Peshtigo Fire is often cited as the deadliest wildfire in U.S. history, occurring in 1871 and resulting in the loss of over 1,500 lives.
What Triggers Wildfire Events?
Wildfire events can be ignited by natural causes like lightning or human activities such as campfires, discarded cigarettes, or arson.
How Do Wildfire Events Affect Air Quality?
Smoke from wildfire events can severely decrease air quality, posing health risks to local populations, particularly respiratory issues.
What Measures Help Prevent Wildfire Events?
Implementing fire breaks, controlled burns, and public education are effective measures against wildfire events, reducing hazards and risks.
Can Wildfire Events Be Beneficial?
Yes, wildfire events can rejuvenate ecosystems by promoting biodiversity, nutrient cycling, and the regeneration of certain plants that rely on fire to thrive.