Understanding Structural Steel Fabrication
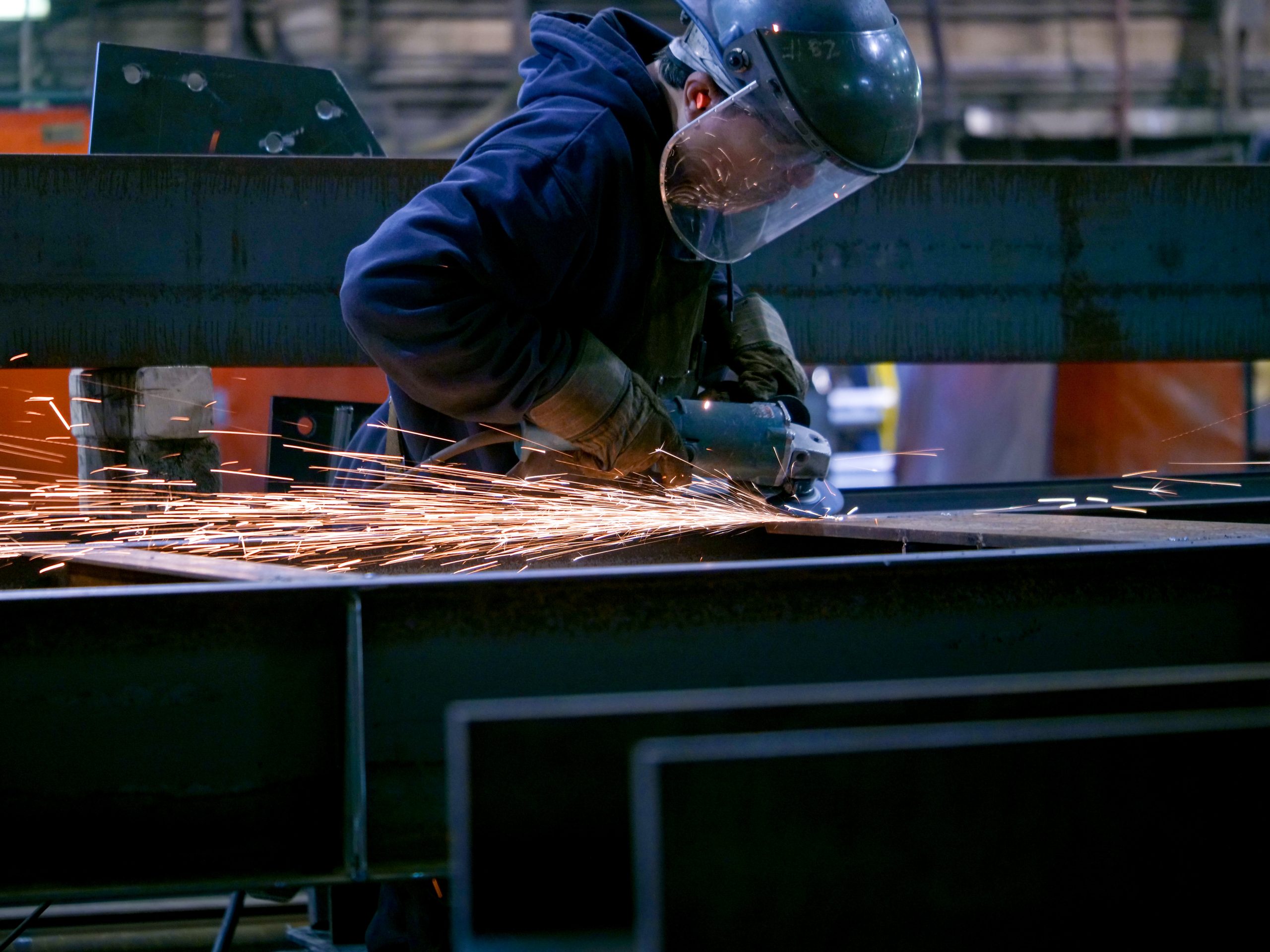
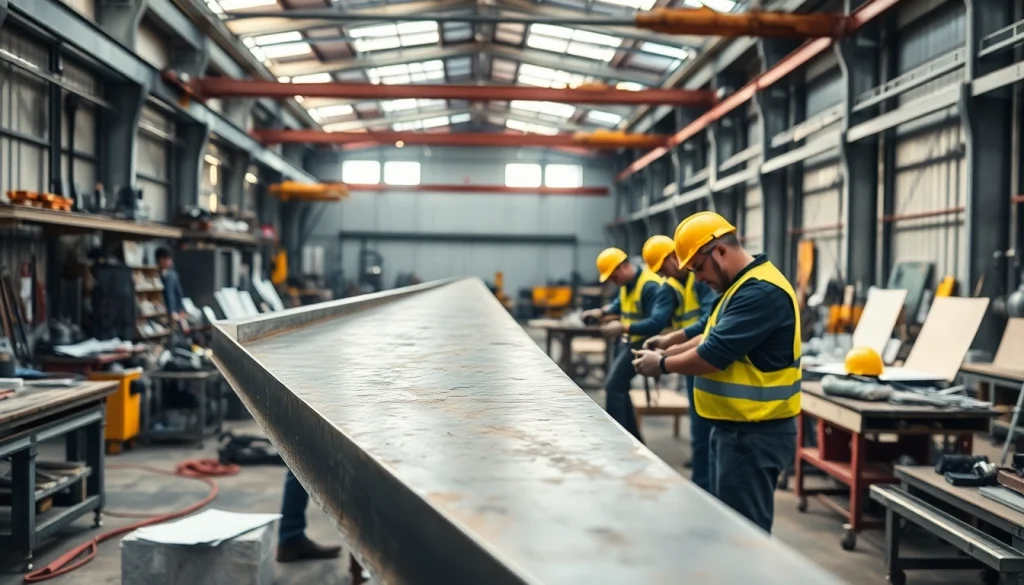
Structural steel fabrication is a crucial process in the construction industry that transforms raw steel into usable structures, extending beyond mere construction to encompass engineering and design intricacies. The process involves several stages, including cutting, shaping, joining, and finishing the steel to meet project specifications. For companies venturing into various engineering projects, understanding the nuances of structural steel fabrication is essential for successful implementations.
What is Structural Steel Fabrication?
Structural steel fabrication entails the construction of steel structures through processes like cutting, welding, and machining. This activity usually entails a transformation of steel stock—flat bars, angles, and plates—into complex shapes tailored for specific applications, ranging from beams and columns to custom fabricated parts for various structures. The final products are recognized for their durability, strength, and load-bearing capabilities, making them integral to modern construction.
Key Benefits of Structural Steel
- Durability: Structural steel stands the test of time, resisting corrosion, weather, and fire effectively.
- Versatility: Its ability to be molded into various shapes and sizes makes it suitable for diverse applications.
- Cost-effectiveness: In comparison with other materials, steel often offers a better longevity-to-cost ratio, leading to lower maintenance expenses.
- Speed of Construction: Prefabricated structural steel components can save significant time on-site compared to traditional construction methods.
Common Applications of Structural Steel Fabrication
Structural steel finds itself in a myriad of applications due to its intrinsic properties. Common areas of use include:
- Commercial Buildings: Skyscrapers and office buildings often utilize structural steel frames for their strength.
- Bridges: Many modern bridges are crafted with steel frameworks for optimal load-bearing capabilities.
- Industrial Facilities: Factories and warehouses extensively employ structural steel for robust structural support.
- Residential Buildings: Steel framing is increasing in popularity due to its robustness and longevity.
Essential Techniques in Structural Steel Fabrication
Cutting and Shaping Methods
The initial phase of structural steel fabrication often involves cutting and shaping raw steel into specified dimensions. Key methods include:
- Laser Cutting: Precision cutting using laser technology provides a clean edge and minimizes material wastage.
- Plasma Cutting: This technique employs hot plasma to cut through metal, offering versatility and efficiency for thick materials.
- Water Jet Cutting: Utilizing high-pressure water combined with abrasive materials achieves finely detailed cuts without heating the steel.
Joining Techniques: Welding vs. Bolting
Joining is a vital aspect of structural steel fabrication. The two primary methods utilized are welding and bolting.
- Welding: This permanent joining method melts the base metals at the joint, allowing them to fuse together upon cooling. It is ideal for applications requiring high structural strength.
- Bolting: A mechanical fastening method, bolting allows for disassembly and is often used in structures that might require future adjustments or repairs.
Finishing Processes for Structural Steel
After fabrication, finishing treatments are essential to enhance the corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal of structural steel. Common finishes include:
- Painting: Applying a protective paint layer guards against rust and improves visual appeal.
- Galvanization: This process coats steel with a layer of zinc, providing exceptional corrosion resistance.
- Coating: Specialty coatings can be applied to meet specific environmental or aesthetic needs.
Best Practices in Structural Steel Fabrication
Safety Standards and Regulations
Ensuring the safety of personnel and compliance with legal regulations is paramount in structural steel fabrication. Industry standards such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) guidelines and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) regulations provide frameworks to minimize risks.
Quality Control Measures
Implementing robust quality control measures throughout the fabrication process is crucial. Techniques include regular inspections, material testing, and adherence to fabrication specifications to guarantee the integrity of the product.
Environmental Considerations in Fabrication
In today’s eco-conscious environment, structural steel fabrication practices should aim for sustainability. Strategies may involve the use of recycled steel, minimal waste generation, and clean manufacturing processes to reduce the environmental footprint.
Innovations in Structural Steel Fabrication
Advanced Technology and Automation
The evolution of technology has transformed structural steel fabrication. Automation in various stages—from robotic welding to automated cutting systems—is enhancing precision and increasing throughput while lowering labor costs.
The Role of 3D Modeling and BIM
3D modeling and Building Information Modeling (BIM) technologies allow engineers and architects to visualize and simulate structures before they are built. This approach not only minimizes errors but also enhances collaboration among stakeholders throughout the construction process.
Future Trends in the Industry
Emerging trends indicate a shift towards more sustainable and efficient practices in structural steel fabrication. The ongoing integration of AI and machine learning, the development of smart materials, and cyclic regeneration processes are opening new avenues for innovation and enhancement in structural efficacy and sustainability.
Measuring Success in Structural Steel Fabrication
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Measuring success in structural steel fabrication is critical in assessing productivity and quality. Defining relevant KPIs includes tracking:
- Material Yield Ratio
- Production Cycle Times
- Quality Assurance Pass Rates
- Cost Variance
Case Studies of Successful Projects
Undertaking successful structural steel projects involves learning from past experiences. Case studies showcasing innovative techniques, effective problem-solving, and collaborative approaches can provide insight and inspiration for future projects.
Continuous Improvement Strategies
Implementing a culture of continuous improvement involves regularly analyzing processes, gathering feedback, and engaging in training. This proactive approach allows companies to stay competitive and adapt to changing market demands, enhancing the effectiveness of structural steel fabrication.